Understanding the Significance of Model Prototypes in Architecture
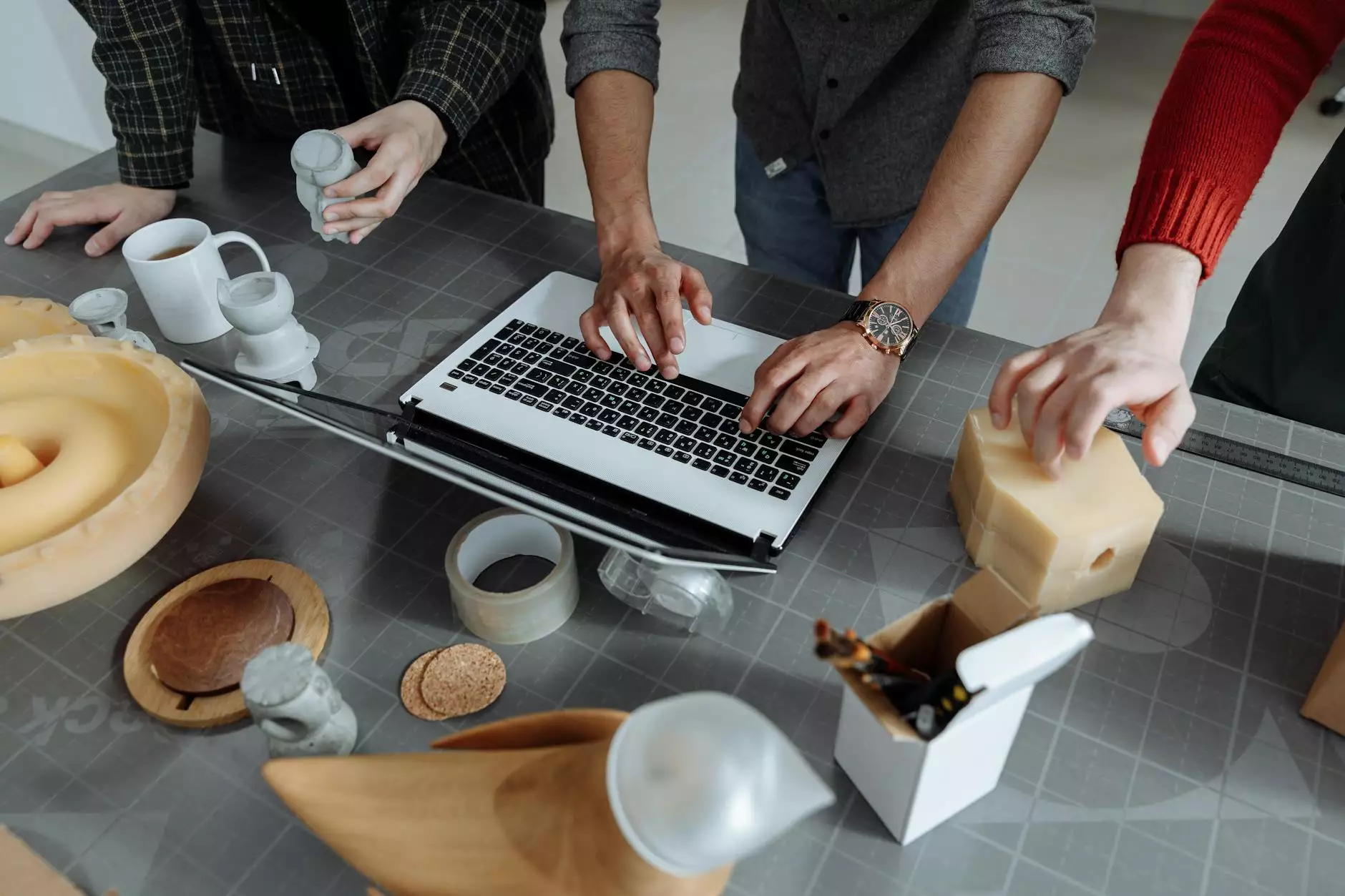

In the world of architecture, the phrase "model prototype" resonates deeply among architects, designers, and builders alike. A model prototype is more than just a small representation of a building; it serves as a critical tool in the design process, providing insights and clarity that drawings and digital models often cannot convey. This article delves into the various aspects of model prototypes, their importance, and how they enhance the architectural design process.
What is a Model Prototype?
A model prototype is a three-dimensional representation of a final design, created to help visualize the project in its physical form. This can include:
- Scale Models: Created to a specific scale, these physical models allow architects and clients to see the proportions and overall structure.
- Virtual Prototypes: These digital representations can simulate how a building interacts with its environment before construction begins.
- Functional Prototypes: Designed to test specific elements of a structure, these prototypes address how features will perform under real-life conditions.
The Role of Model Prototypes in Architectural Design
In architectural design, a model prototype plays several key roles that significantly contribute to the overall success of a project:
1. Enhancing Visualization
One of the primary benefits of using model prototypes is their ability to enhance visualization. Clients and stakeholders often find it challenging to interpret two-dimensional drawings. A model prototype helps bridge this gap by providing a tangible representation of the design, making it easier for everyone involved to understand the project.
2. Identifying Potential Issues Early
Model prototypes allow architects to spot potential problems during the design phase. By examining the physical model, architects can assess the feasibility of certain features and make adjustments before the construction phase begins. This proactive approach minimizes costly changes later in the project lifecycle.
3. Facilitating Communication
Effective communication is essential in any architectural project. Model prototypes serve as a visual communication tool, helping architects convey complex ideas to clients, contractors, and other stakeholders clearly and effectively. This fosters collaboration and ensures everyone is on the same page.
4. Testing Design Concepts
Prototyping allows architects to test various design concepts in a physical form. This can include experimenting with materials, colors, and structural elements. A model prototype not only proves helpful in aesthetic considerations but also enables testing for functionality, light flow, and spatial dynamics.
Types of Model Prototypes in Architecture
There are various types of model prototypes used in architectural practice, each serving unique purposes:
1. Physical Scale Models
These are tangible models built to a specific scale, showcasing how a structure will appear in real life. They can range from small, simple models used for initial design concepts to large, intricate ones that include detailed landscaping and surrounding structures.
2. Concept Models
Concept models are often used in the early phases of the design process. They focus on the fundamental ideas behind a project's form, space, and experience rather than the specifics. These models encourage creativity and exploration.
3. Presentation Models
These models are typically highly refined and detailed, used during presentations to stakeholders or clients. They aim to impress and effectively communicate the final design vision of the project.
4. Built Models
These prototypes are constructed to test the actual building methods and materials that will be used on the project site, allowing architects and builders to identify any issues with the design before construction begins.
Benefits of Using Model Prototypes in Architecture
Utilizing model prototypes presents numerous advantages to architectural best practices, such as:
- Cost Efficiency: By identifying design flaws early in the process, model prototypes can save significant amounts of money that would otherwise be spent on rectifying issues post-construction.
- Improved Client Satisfaction: Clients who can visualize the end product through models tend to feel more confident and satisfied with the design process.
- Streamlined Feedback: Physical models provide a clear reference point for feedback, making it easier to gather insights from clients and stakeholders.
- Innovation and Creativity: Experimenting with designs using prototypes encourages innovative solutions and creative approaches to architectural challenges.
Best Practices for Creating Effective Model Prototypes
To maximize the benefits of model prototypes, architects should consider the following best practices:
1. Define Clear Objectives
Before starting the model, architects should set clear objectives. What specific aspects of the design need representation? Are you focusing on visual appeal, functionality, or structural integrity? Clear goals will guide the creation process.
2. Choose the Right Materials
Using appropriate materials is essential for effective model prototypes. Different materials can convey different aspects; for instance, cardboard is excellent for initial conceptual models, while acrylic and wood can be used for more refined models.
3. Incorporate Feedback Loops
Involve your team and clients in the feedback process. Presenting model prototypes for review and critique can lead to valuable insights and improvements that can enhance the final design.
4. Leverage Technology for Virtual Prototypes
Modern technology allows architects to create virtual prototypes using software tools like CAD and 3D modeling applications. Incorporating both physical and virtual models provides comprehensive insights and perspectives on the design.
Case Studies: Successful Use of Model Prototypes
Many renowned architectural firms have effectively leveraged model prototypes in their projects:
1. The Sydney Opera House
One of the most iconic buildings in the world, the Sydney Opera House, utilized a variety of models throughout its design process. The original concept involved numerous scale models that allowed the designers to experiment with its unique shell-like forms, leading to a groundbreaking architectural masterpiece.
2. The Guggenheim Museum Bilbao
Frank Gehry's Guggenheim Museum in Bilbao involved extensive prototyping at different scales. The fluid, organic shapes of the building were adjusted and perfected through both physical and digital model prototypes, demonstrating the importance of prototyping in executing revolutionary designs.
Conclusion
The use of model prototypes in architecture is essential in enhancing design communication, facilitating creativity, and mitigating project risks. By embracing the art of model making, architects can ensure that their visions translate accurately from concept to reality. In an industry where precision and innovation are crucial, model prototypes stand out as invaluable resources that bridge the gap between imagination and execution. The potential to explore, experiment, and visualize makes model prototypes a non-negotiable tool that every architect should utilize to achieve success in their projects.
For more information on enhancing your architectural practices through effective modeling techniques, explore additional resources at architectural-model.com.